인접 행렬로 BFS 구현
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
struct Vertex
{
// int data;
};
vector<Vertex> vertices;
vector<vector<int>> adjacent;
vector<vector<int>> adjacent2;
vector<bool> visited;
vector<bool> discovered;
void CreateGraph()
{
vertices.resize(6);
discovered.resize(6);
adjacent = vector<vector<int>>(6);
adjacent2 = vector<vector<int>>(6);
// 인접 리스트 사용 그래프 구현
adjacent[0].push_back(1);
adjacent[0].push_back(3);
adjacent[1].push_back(0);
adjacent[1].push_back(2);
adjacent[1].push_back(3);
adjacent[3].push_back(4);
adjacent[5].push_back(4);
// 인접 행렬 사용 그래프 구현
adjacent2 = vector<vector<int>>
{
{0,1,0,1,0,0},
{1,0,1,1,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,1,0},
};
}
// 인접 행렬을 이용한 Bfs 구현
void Bfs2(int here)
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(here);
discovered[here] = true;
while (q.empty() == false)
{
here = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Visited : " << here << endl;
for (int there = 0; there < 6; there++)
{
if (adjacent2[here][there] == false)
{
continue;
}
if (discovered[there])
{
continue;
}
q.push(there);
discovered[there] = true;
}
}
// 디버깅 용 더미 코드
int a = 3;
}
// 독립된 노드인 5번 노드를 탐색하기 위해서 모든 노드를 시작점으로 for문 돌리기
void BfsAll2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
{
if (discovered[i] == false)
{
Bfs2(i);
}
}
}
시작점으로부터 각 노드 사이 거리 측정 및 역추적
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
struct Vertex
{
// int data;
};
vector<Vertex> vertices;
vector<vector<int>> adjacent;
vector<vector<int>> adjacent2;
vector<bool> visited;
vector<bool> discovered;
void CreateGraph()
{
vertices.resize(6);
discovered.resize(6);
adjacent = vector<vector<int>>(6);
adjacent2 = vector<vector<int>>(6);
// 인접 리스트 사용 그래프 구현
adjacent[0].push_back(1);
adjacent[0].push_back(3);
adjacent[1].push_back(0);
adjacent[1].push_back(2);
adjacent[1].push_back(3);
adjacent[3].push_back(4);
adjacent[5].push_back(4);
// 인접 행렬 사용 그래프 구현
adjacent2 = vector<vector<int>>
{
{0,1,0,1,0,0},
{1,0,1,1,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,1,0},
};
}
// 시작점으로부터 노드 간에 거리 측정
void Bfs3(int here)
{
// 기존 Bfs 코드를 변경하지 않고 추가만 한다.
//누구에 의해 발견 되었는지?
vector<int> parent(6, -1);
// 시작점에서 얼만큼 떨어져 있는지?
vector<int> distance(6, -1);
queue<int> q;
q.push(here);
discovered[here] = true;
// 맨 처음 시작점을 기준으로 자신이 스스로를 발견했다.
parent[here] = here;
// 시작 노드와 처음 발견한 노드가 같으므로 거리 0
distance[here] = 0;
while (q.empty() == false)
{
here = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Visited : " << here << endl;
for (int there : adjacent[here])
{
if (discovered[there])
{
continue;
}
q.push(there);
discovered[there] = true;
// here 번째 노드에 의해 there 번째 노드가 발견 되어짐
parent[there] = here;
// here 노드와 시작점 노드 사이 거리에 + 1 : here 이 there 을 발견했기 때문에
distance[there] = distance[here] + 1;
}
}
// 디버깅 용 더미 코드
int a = 3;
}
int main()
{
CreateGraph();
discovered = vector<bool>(6, false);
cout << "\n";
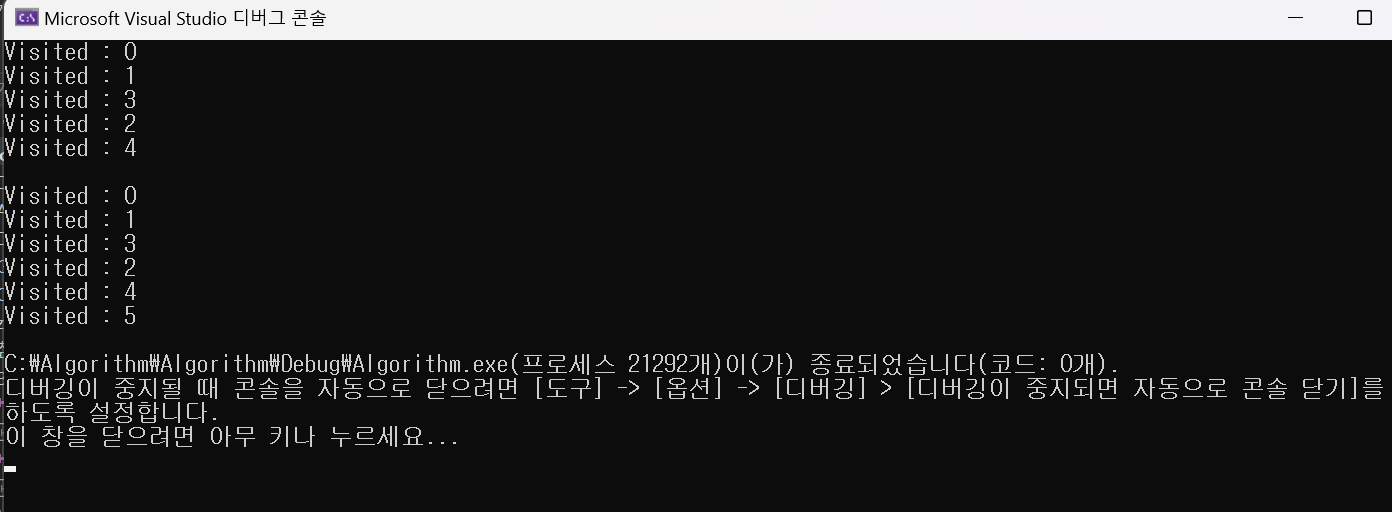
Bfs3(0);
}
여기서 distance 를 확인하면 시작 노드로부터 각 노드들의 거리를 측정할 수 있다.

0번 노드를 시작 노드로 하였을 때 4번 노드는 0번 노드와 2만큼 거리차이가 나고 1번 노드는 시작 노드와 1만큼 거리 차이가 난다. 5번 노드는 단절되어 있다.{5번에서 4번으로가는 단방향 노드}
parent 를 확인하여 경로를 역추적 할 수 있다.
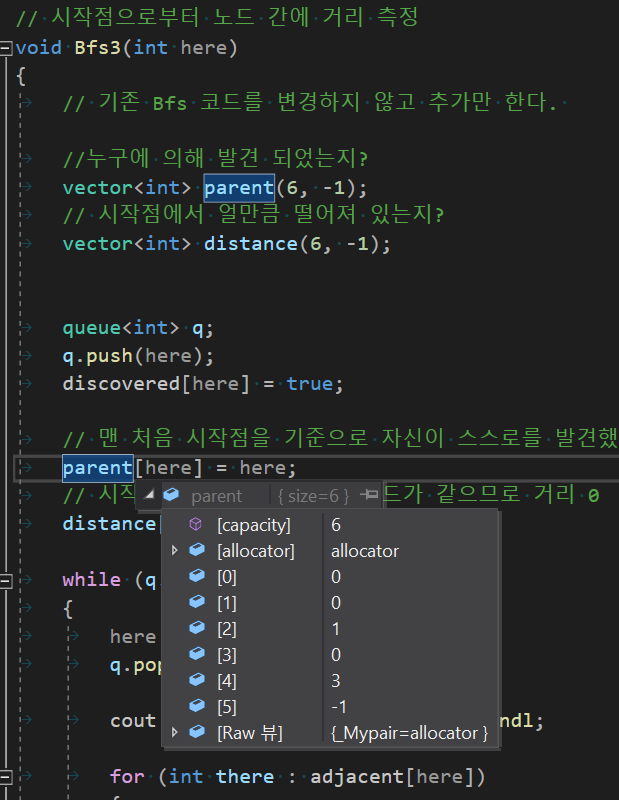
4번 노드는 3번 노드가 발견하였으며, 3번 노드는 0번 노드가 발견하였다.
즉, 0번에서 4번으로 가는 경로는 0 → 3 → 4 번 노드 순인 것을 역추적 가능하다.
'자료구조 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 이진트리 와 힙 이론 (0) | 2024.05.29 |
|---|---|
| 트리 (0) | 2024.05.29 |
| BFS 인접 리스트 (0) | 2024.05.29 |
| DFS (0) | 2024.05.29 |
| 그래프 구현 (0) | 2024.05.29 |


